Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMQ8JIK)
| Drug Name |
Chenodiol
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
474-25-9; Chenix; Chenic acid; Chenodeoxycholate; Gallodesoxycholic acid; Chendol; Chenodesoxycholic acid; Cdca; Chenofalk; Anthropodeoxycholic acid; Anthropodesoxycholic acid; Anthropododesoxycholic acid; Chenodesoxycholsaeure; Xenbilox; Henohol; Chenique Acid; Chenodiol [USAN]; 3alpha,7alpha-Dihydroxy-5beta-cholan-24-oic acid; Sodium chenodeoxycholate; Acido chenodeoxicholico; Chenodesoxycholsaeure [German]; Acide chenodeoxycholique; 7-alpha-Hydroxylithocholic acid; Acidum chenodeoxycholicum
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
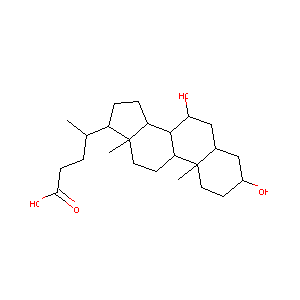 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 392.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 4.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Cholelithiasis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | DC11 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Chenodiol (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 3 | Lithocholic acid decreases expression of bile salt export pump through farnesoid X receptor antagonist activity. J Biol Chem. 2002 Aug 30;277(35):31441-7. | ||||
| 4 | Identification of human hepatic cytochrome p450 enzymes involved in the biotransformation of cholic and chenodeoxycholic acid. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008 Oct;36(10):1983-91. | ||||
| 5 | Human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)1A3 enzyme conjugates chenodeoxycholic acid in the liver. Hepatology. 2006 Nov;44(5):1158-70. | ||||
| 6 | Conversion of chenodeoxycholic acid to cholic acid by human CYP8B1. Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 24;400(5):625-628. | ||||
| 7 | In the search for specific inhibitors of human 11beta-hydroxysteroid-dehydrogenases (11beta-HSDs): chenodeoxycholic acid selectively inhibits 11beta-HSD-I. Eur J Endocrinol. 2000 Feb;142(2):200-7. | ||||
| 8 | Lack of response to chenodeoxycholic acid in obese and non-obese patients. Role of cholesterol synthesis and possible response to ursodeoxycholic acid. Gut. 1980 Dec;21(12):1082-6. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.12.1082. | ||||
| 9 | Potency of individual bile acids to regulate bile acid synthesis and transport genes in primary human hepatocyte cultures. Toxicol Sci. 2014 Oct;141(2):538-46. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu151. Epub 2014 Jul 23. | ||||
| 10 | Chenodeoxycholic acid significantly impacts the expression of miRNAs and genes involved in lipid, bile acid and drug metabolism in human hepatocytes. Life Sci. 2016 Jul 1;156:47-56. | ||||
| 11 | Relationship of human liver dihydrodiol dehydrogenases to hepatic bile-acid-binding protein and an oxidoreductase of human colon cells. Biochem J. 1996 Jan 15;313 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):373-6. | ||||
| 12 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 13 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 14 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 15 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 16 | Product Information. Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 17 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 19 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
